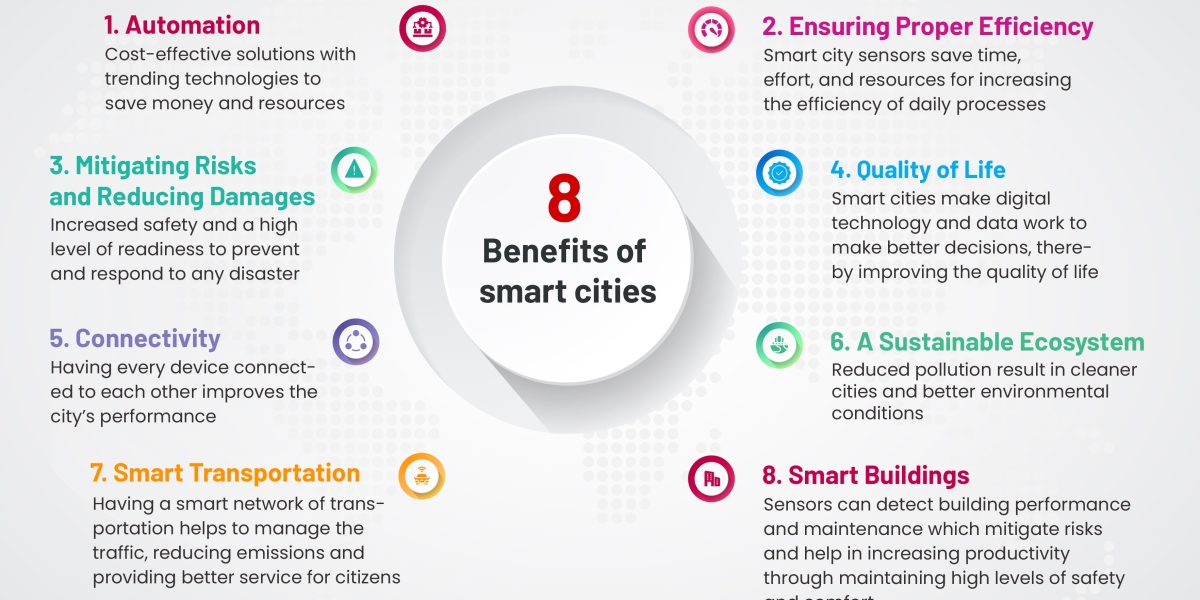
1. Improved Public Services
Smart city systems enhance the delivery of essential services such as waste collection, public transit, utilities, and emergency response. By using real-time data, cities can allocate resources more efficiently and respond to citizens’ needs faster.
Examples:
Dynamic bus routes based on commuter density
Automated street cleaning schedules
Digital platforms for citizen complaints and issue tracking
2. Enhanced Public Safety and Security
With intelligent surveillance systems, facial recognition, and emergency alert platforms, smart cities can proactively monitor risks and respond quickly to threats.
Examples:
Smart CCTV with motion detection and AI analysis
Gunshot detection systems
Integrated command centers for rapid crisis coordination
3. Sustainability and Environmental Protection
Smart cities help reduce carbon emissions, promote renewable energy, and manage natural resources more efficiently. These efforts are critical to fighting climate change and improving urban livability.
Examples:
Smart grids that balance energy loads
Solar-powered public infrastructure
Real-time air and water quality monitoring
4. Economic Efficiency and Cost Savings
By reducing waste, automating operations, and optimizing infrastructure use, smart city solutions lead to significant cost savings for both governments and citizens.
Examples:
Lower electricity bills through smart meters
Reduced fuel consumption via optimized traffic systems
Predictive maintenance that prevents infrastructure failures
5. Better Mobility and Transportation
Intelligent transportation systems make travel more efficient, reduce traffic congestion, and promote the use of public transport and non-motorized options like cycling.
Examples:
Real-time traffic updates and alternate route suggestions
Smart parking systems
Shared micro-mobility solutions (e-scooters, bike rentals)
6. Greater Citizen Engagement
Smart city platforms offer mobile apps, e-portals, and SMS-based services that make it easier for residents to interact with their governments, submit feedback, and participate in decision-making.
Examples:
Digital town hall meetings
E-governance platforms for service applications
Voting and polling apps for community input
Real-World Use Cases and Examples
? Case 1: Barcelona, Spain
Barcelona is a global pioneer in smart city innovation. The city implemented a network of IoT sensors to monitor traffic, air quality, and energy consumption. It also deployed smart irrigation systems in parks, reducing water usage by 25%.
Key Highlights:
Smart streetlights with motion sensors
City-wide fiber network and free Wi-Fi
Smart parking spots with real-time availability
? Case 2: Singapore
Singapore’s Smart Nation initiative integrates data from sensors across the city to manage traffic, monitor public safety, and enhance public services. The city-state also launched the Virtual Singapore digital twin for urban planning.
Key Highlights:
Facial recognition in public spaces (with privacy safeguards)
Smart eldercare and healthcare tracking
AI for predicting dengue outbreaks based on climate patterns
? Case 3: Makati City, Philippines
As part of Metro Manila, Makati City implemented a centralized command center that integrates CCTVs, traffic monitoring, disaster response, and emergency services. Suniway and similar integrators are helping expand such platforms.
Key Highlights:
CCTV surveillance linked to AI for license plate recognition
Flood sensors integrated with SMS alert systems
E-governance platform for document requests and complaints
? Case 4: Songdo, South Korea
Songdo is one of the world’s most advanced smart cities, built from scratch with IoT infrastructure embedded in its design. Everything from energy use to waste management is controlled via centralized systems.
Key Highlights:
Pneumatic waste collection systems
Smart buildings with environmental controls
Sensors in every streetlight and intersection