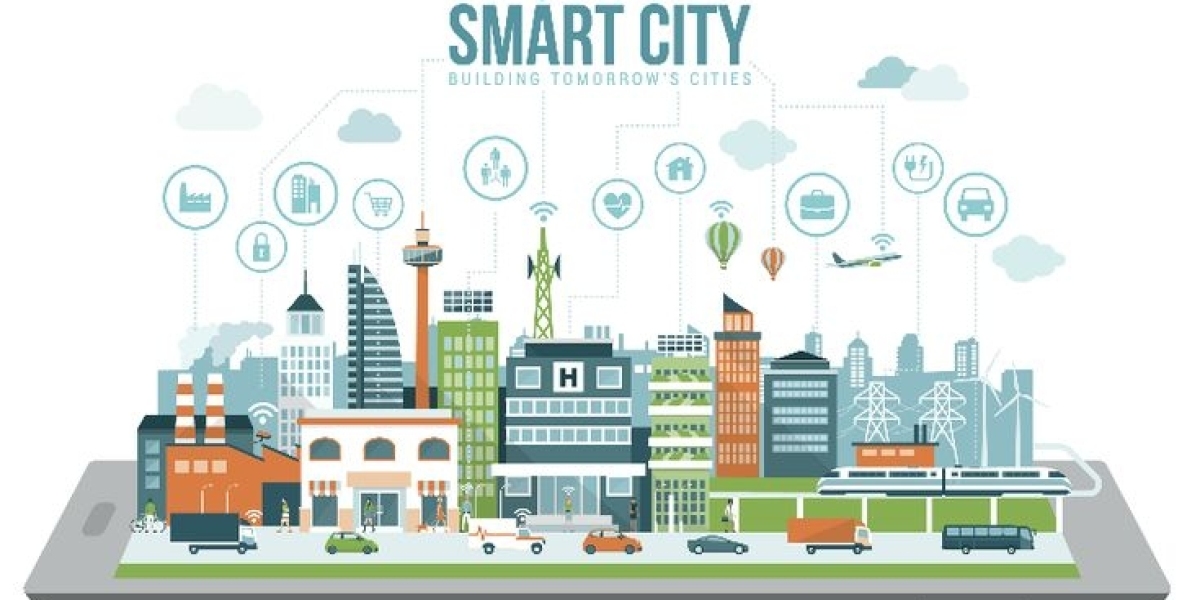
Core Technologies Behind Smart Cities
At the heart of every smart city lies a network of interconnected technologies. These foundational components work together to collect, transmit, analyze, and act on data across a variety of urban domains. Below are the core technologies that power smart city solutions:
1. Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT devices, including sensors, meters, and smart cameras, are embedded throughout the city to monitor traffic, air quality, waste levels, energy usage, and more. These devices collect real-time data that feed into central management systems.
Examples:
Smart streetlights that adjust brightness based on activity
Waste bins that signal when they’re full
Smart water meters for usage and leak detection
2. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning
AI algorithms analyze vast amounts of urban data to identify patterns, predict trends, and optimize systems. From traffic flow forecasting to predictive maintenance, AI enhances efficiency and decision-making.
Examples:
Facial recognition for public safety
AI chatbots for city services
Energy demand forecasting
3. Big Data Analytics
Big data tools allow cities to extract meaningful insights from massive datasets. This empowers city planners and decision-makers to respond faster to issues, allocate resources more effectively, and improve citizen services.
Examples:
Mobility analytics for transit planning
Real-time air quality dashboards
Heatmaps of electricity consumption
4. Cloud Computing
Cloud infrastructure ensures that data is accessible, scalable, and secure. It allows city systems to be managed remotely, updated in real-time, and backed up with minimal physical infrastructure.
Examples:
Cloud-hosted e-governance platforms
Remote access to municipal databases
Disaster recovery and business continuity
5. 5G and Advanced Connectivity
High-speed, low-latency networks like 5G are essential for transmitting data between devices and systems. They enable the real-time performance required by many smart city applications, such as autonomous vehicles and remote medical services.
Examples:
5G-enabled smart traffic lights
Telemedicine in underserved areas
Mobile command centers for emergency response
6. Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
GIS technology allows cities to visualize, analyze, and manage spatial data. It’s instrumental in urban planning, utility mapping, and emergency preparedness.
Examples:
Flood risk mapping
Land use optimization
Real-time asset tracking