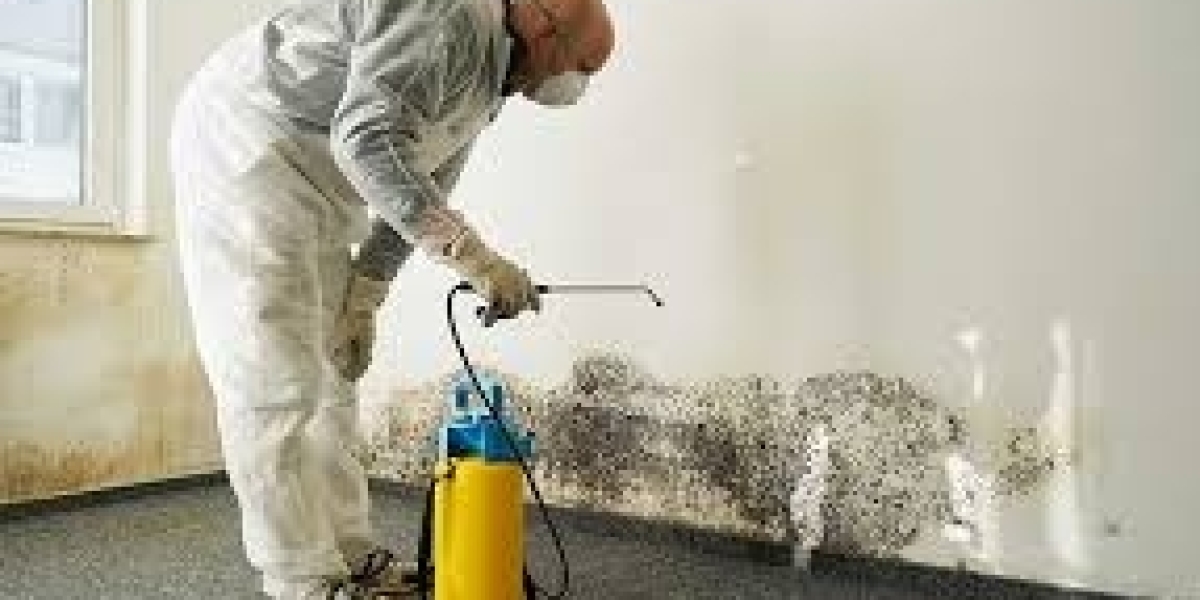
Mold remediation is far more than wiping visible mold from a wall. It is a structured, scientific process designed to identify, contain, remove, and prevent mold growth while safeguarding both building occupants and the structure itself. When performed correctly, mold remediation restores indoor air quality, protects property value, and reduces serious health risks.
This article explains what mold remediation is, how it differs from simple mold removal, why professional remediation matters, and what best practices ensure long-term success.
What Is Mold and Why Is It Dangerous?
Mold is a naturally occurring fungus that thrives in moist environments. It reproduces by releasing microscopic spores into the air, which can settle and grow wherever moisture is present—behind walls, under flooring, in HVAC systems, and inside insulation.
Health Risks of Mold Exposure
Exposure to mold can cause or worsen:
Allergic reactions (sneezing, rashes, watery eyes)
Asthma attacks and respiratory distress
Chronic sinus infections
Fatigue and headaches
Immune system complications
Certain molds, such as Stachybotrys chartarum (often called black mold), produce mycotoxins that may cause severe health effects with prolonged exposure.
Mold Removal vs. Mold Remediation: Understanding the Difference
Many people use the terms interchangeably, but they are not the same.
Mold Removal
Focuses only on visible mold
Often involves surface cleaning or painting over mold
Does not address moisture sources
High risk of mold returning
Mold Remediation
Identifies the source of moisture
Contains airborne spores
Removes contaminated materials
Cleans and treats affected areas
Prevents future mold growth
True remediation eliminates the conditions that allow mold to grow, not just the mold you can see.
Common Causes of Mold Growth
Understanding the root cause is essential for successful remediation.
Water leaks (plumbing, roofs, appliances)
Flooding or water intrusion
High indoor humidity (above 60%)
Poor ventilation
Condensation in crawl spaces and attics
HVAC system failures
Without correcting these issues, mold will almost certainly return.
The Professional Mold Remediation Process
1. Mold Inspection and Assessment
Certified technicians inspect the property using moisture meters, infrared cameras, and air sampling (if needed) to identify affected areas and contamination levels.
2. Containment
To prevent mold spores from spreading:
Plastic sheeting isolates contaminated areas
Negative air pressure systems are installed
HEPA air scrubbers filter airborne spores
This step is critical to protecting unaffected areas of the building.
3. Air Filtration
High-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters remove mold spores and other contaminants from the air, improving indoor air quality throughout the remediation process.
4. Removal of Mold-Contaminated Materials
Porous materials such as:
Drywall
Carpet
Insulation
Ceiling tiles
often must be removed and disposed of safely if contamination is severe.
5. Cleaning and Disinfection
Non-porous and semi-porous materials are cleaned using:
Antimicrobial solutions
HEPA vacuuming
Specialized mold-inhibiting treatments
6. Drying and Dehumidification
Industrial dehumidifiers and air movers eliminate remaining moisture, preventing regrowth.
7. Restoration and Prevention
The final stage includes repairing damaged areas and implementing preventative measures such as:
Improved ventilation
Moisture barriers
Humidity control systems
Can Mold Remediation Be Done DIY?
Small, surface-level mold (less than 10 square feet) can sometimes be handled by homeowners using proper PPE and cleaning agents. However, DIY remediation is not recommended when:
Mold covers large areas
Mold is inside walls or HVAC systems
Occupants have respiratory conditions
Water damage is extensive or recurring
Improper handling can spread spores, worsen contamination, and increase health risks.
The Importance of Hiring Certified Professionals
Professional mold remediation companies:
Follow EPA and IICRC standards
Use specialized equipment
Understand building science and moisture dynamics
Provide documentation for insurance and real estate transactions
Certification ensures remediation is done safely, legally, and effectively.
Preventing Mold After Remediation
Long-term prevention is just as important as removal.
Best Prevention Practices
Maintain indoor humidity below 50%
Fix leaks immediately
Improve ventilation in kitchens and bathrooms
Use dehumidifiers in damp areas
Schedule regular property inspections
Prevention protects your investment and minimizes future remediation costs.
Mold Remediation and Property Value
Unresolved mold issues can:
Reduce property value
Delay real estate transactions
Lead to failed inspections
Increase liability risks
Proper remediation restores confidence for buyers, tenants, and insurers while ensuring compliance with health and safety standards.
Final Thoughts
Mold remediation is a critical process that protects both human health and structural integrity. Unlike simple mold removal, professional remediation addresses the root cause of contamination, prevents recurrence, and restores safe indoor environments.
If you suspect mold in your home or commercial property, acting quickly and choosing qualified remediation professionals can save time, money, and long-term health complications.
Mold is not just a cosmetic issue—it’s an environmental hazard that deserves expert attention.