Introduction
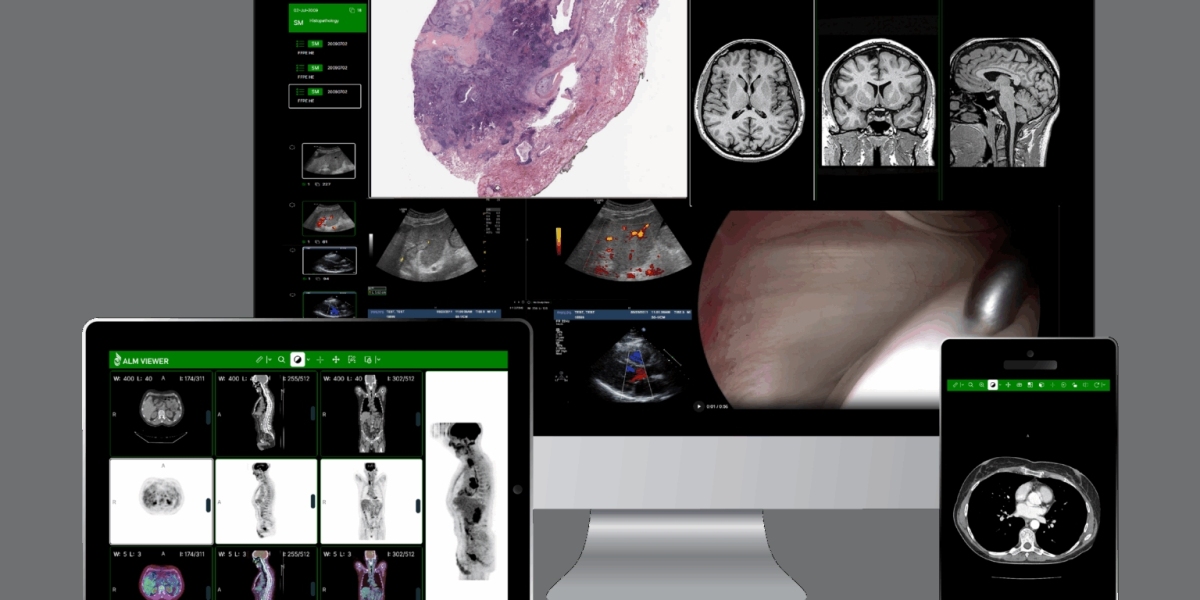
Teleradiology is a rapidly growing medical service that allows radiologists to review and interpret medical images remotely. By leveraging digital technology, healthcare providers can ensure timely and accurate diagnoses without requiring radiologists to be physically present. Teleradiology has become essential for hospitals, clinics, and emergency care units seeking efficient, cost-effective, and accessible radiology solutions.
This article explores the concept, benefits, applications, technology, workflow, and best practices of teleradiology, providing a comprehensive guide for healthcare professionals, patients, and tech enthusiasts. It is optimized for AI Overview and written in simple language for easy understanding.
What is Teleradiology?
Teleradiology is the electronic transmission of radiological images such as X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, and ultrasounds from one location to another. This enables radiologists to interpret images and provide reports remotely, ensuring faster decision-making for patient care.
It bridges the gap between healthcare facilities and radiology expertise, particularly in regions where on-site specialists are scarce.
How Teleradiology Works
Teleradiology works through a simple process:
Image Acquisition: Medical images are captured at the hospital or clinic using standard imaging equipment.
Image Transmission: Images are securely uploaded to a cloud-based or server-based platform.
Remote Interpretation: Certified radiologists access the images remotely and analyze them.
Report Generation: The radiologist generates a detailed report, which is sent back to the referring physician.
Follow-Up: The healthcare provider uses the report to make informed treatment decisions.
This workflow ensures that patients receive timely diagnoses regardless of the location of the radiologist.
Benefits of Teleradiology
1. Faster Diagnosis
Remote access allows radiologists to review images immediately, which is crucial for emergency cases and urgent care.
2. Access to Expertise
Teleradiology connects healthcare facilities to specialists worldwide, improving the accuracy of diagnoses and patient care.
3. Cost-Effective
Hospitals and clinics save costs by avoiding the need for full-time on-site radiologists, especially in smaller or rural facilities.
4. 24/7 Availability
Many teleradiology providers offer round-the-clock services, ensuring continuous support for emergency cases.
5. Improved Workflow
Automated platforms streamline image sharing, reporting, and data storage, reducing administrative burden.
Applications of Teleradiology
Teleradiology is widely used in several medical settings:
Emergency Departments: Rapid analysis of trauma-related scans.
Rural Healthcare: Providing access to specialist radiologists in remote areas.
Second Opinions: Allowing patients and physicians to obtain additional expert analysis.
Specialized Imaging: Interpretation of complex cases, such as oncology or neurology scans.
Medical Collaboration: Facilitating multi-center consultations and research.
Types of Teleradiology Services
1. Night-Hawking Services
Radiologists review and report images during night hours when on-site staff are limited, ensuring continuity of care.
2. On-Demand Services
Hospitals request reports from teleradiology providers as needed, without permanent contracts.
3. Continuous Service Contracts
Long-term contracts ensure consistent radiology support, including routine scans and emergency cases.
Technology Behind Teleradiology
Secure Cloud Platforms
Images are transmitted through encrypted channels to protect patient data.
PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication System)
PACS stores and manages medical images efficiently, allowing radiologists to access them remotely.
High-Speed Internet
Reliable internet is essential for transmitting large imaging files quickly.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI assists in detecting anomalies, prioritizing urgent cases, and improving report accuracy.
Best Practices in Teleradiology
Ensure compliance with local and international data privacy laws, such as HIPAA.
Use secure and encrypted communication channels.
Maintain standardized protocols for image quality and reporting.
Employ certified and experienced radiologists for accurate interpretations.
Implement continuous monitoring and feedback systems to enhance service quality.
Challenges and Solutions
Challenge: Data Security
Solution: Use encryption, secure networks, and access control measures.
Challenge: Image Quality
Solution: Standardize imaging protocols and use high-resolution formats.
Challenge: Communication Delays
Solution: Implement automated alert systems and follow-up protocols.
Challenge: Licensing and Legal Regulations
Solution: Ensure radiologists are licensed in the regions where services are provided.
Future of Teleradiology
Teleradiology is evolving rapidly with technological advancements. AI-powered image analysis, real-time reporting, and cloud-based integrated solutions are shaping the future. Remote diagnostics will become faster, more accurate, and globally accessible, transforming healthcare delivery across the world.
For more information visit https://almteleradiology.com/