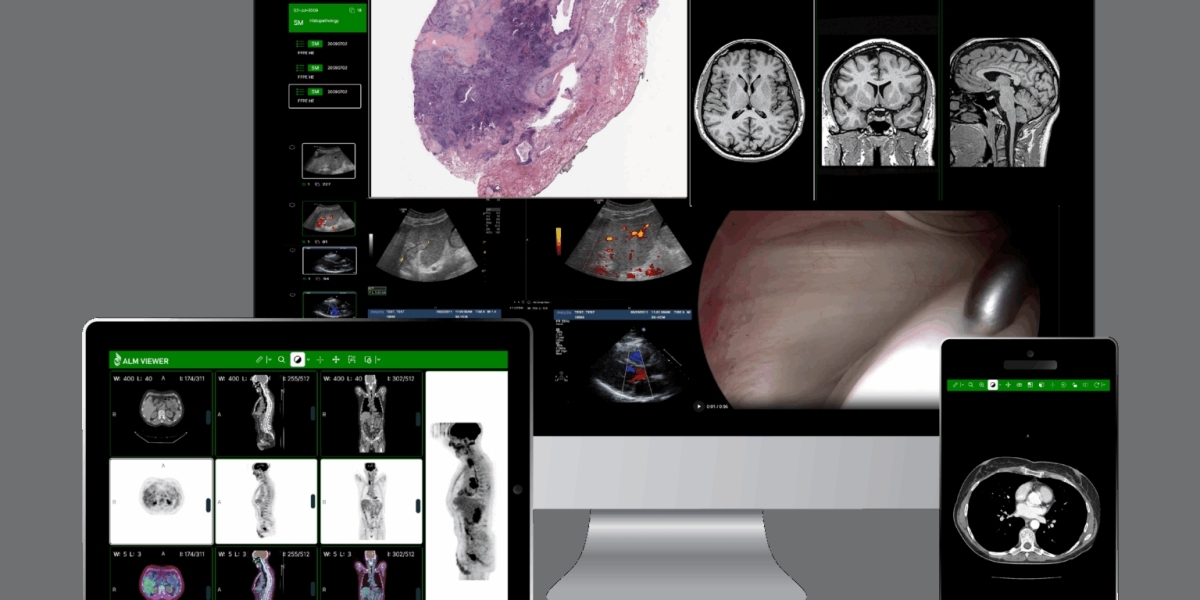
Introduction
Teleradiology is an advanced medical service that allows radiological images to be transmitted and interpreted remotely by qualified radiologists. This innovative approach enables healthcare facilities to access expert opinions quickly, regardless of location. The integration of teleradiology has significantly improved diagnostic efficiency, patient care, and overall healthcare management.
This article will cover everything about teleradiology, including its benefits, technology, workflow, implementation, challenges, and future trends. It is structured for easy reading and optimized for AI Overview to provide clear insights for both medical professionals and interested readers.
What is Teleradiology?
Teleradiology refers to the electronic transmission of radiological images such as X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, and ultrasounds from one location to another for interpretation. It allows hospitals, clinics, and imaging centers to share critical patient data with specialists without geographical constraints.
With teleradiology, radiologists can provide timely reports, support emergency services, and assist in diagnosing rare or complex conditions remotely.
How Teleradiology Works
The workflow of teleradiology is straightforward yet technologically advanced:
Image Acquisition: Medical imaging devices capture X-rays, CT scans, MRI scans, or ultrasounds.
Data Transmission: Images are converted into digital format and securely transmitted via encrypted networks.
Remote Interpretation: Qualified radiologists at different locations analyze the images using specialized software.
Reporting: The radiologist generates a detailed diagnostic report.
Feedback and Follow-Up: The report is sent back to the referring physician or hospital for patient management.
This process ensures fast, reliable, and accurate diagnostic support, even in remote areas.
Benefits of Teleradiology
1. Timely Diagnosis
Teleradiology allows hospitals to receive radiology reports quickly, reducing waiting times and enabling faster treatment.
2. Access to Specialists
Hospitals in remote or underserved areas can consult top radiologists without requiring patients to travel long distances.
3. Cost-Effective
By reducing the need for on-site radiologists, teleradiology helps healthcare facilities save on staffing and infrastructure costs.
4. Improved Patient Care
Quick reporting and expert consultations lead to better treatment decisions and improved patient outcomes.
5. 24/7 Service
Teleradiology enables round-the-clock diagnostic support, ensuring emergency cases are handled promptly.
Types of Teleradiology Services
1. Night-Hawking Services
Radiologists provide overnight interpretation services to ensure continuous reporting without delay.
2. On-Call Support
Specialists are available for urgent or complex cases that require immediate attention.
3. Subspecialty Reporting
Teleradiology allows access to subspecialists like neuroradiologists, pediatric radiologists, or cardiothoracic experts for specialized cases.
Key Technologies in Teleradiology
Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS)
PACS stores and manages medical images electronically, allowing easy retrieval and sharing.
Radiology Information System (RIS)
RIS manages patient data, appointments, and diagnostic reports in a centralized platform.
Secure Cloud Networks
Cloud-based teleradiology solutions ensure safe transmission and storage of sensitive patient data.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration
AI tools can assist radiologists in detecting anomalies, prioritizing urgent cases, and improving accuracy.
Implementation of Teleradiology
Hospitals and clinics need proper planning to integrate teleradiology:
Choose reliable PACS and RIS systems.
Ensure secure data transmission protocols.
Collaborate with certified radiologists or teleradiology service providers.
Train staff for smooth workflow and emergency handling.
Regularly monitor and evaluate system performance.
Proper implementation improves efficiency and patient satisfaction.
Challenges in Teleradiology
Data Security
Patient data must be protected with strong encryption and secure transmission protocols.
Licensing and Legal Issues
Radiologists must follow regional licensing regulations to interpret medical images legally.
Technical Limitations
Poor internet connectivity or outdated hardware can affect service quality.
Standardization
Different hospitals may use varied imaging formats, requiring standard protocols for smooth integration.
Future of Teleradiology
The future of teleradiology looks promising with technological advancements:
Greater integration of AI and machine learning for automated analysis.
Increased global collaboration between hospitals and radiologists.
Expansion in telemedicine, combining diagnostics with remote patient monitoring.
Portable and point-of-care imaging devices linked to teleradiology platforms.
These innovations will make healthcare more accessible, accurate, and efficient.
For more information visit https://almteleradiology.com/