Introduction: What Is Structured Cabling?
Why Structured Cabling Is Crucial for Modern Infrastructure
Components of a Structured Cabling System
Benefits for Businesses, Schools, and Government
Structured Cabling Standards in the Philippines
Structured Cabling Use Cases (Offices, Data Centers, Smart Cities)
How to Choose a Structured Cabling Provider
Top Structured Cabling Providers in the Philippines (2025)
FAQs About Structured Cabling
Conclusion: Build a Future-Ready Network
1. Introduction: What Is Structured Cabling?
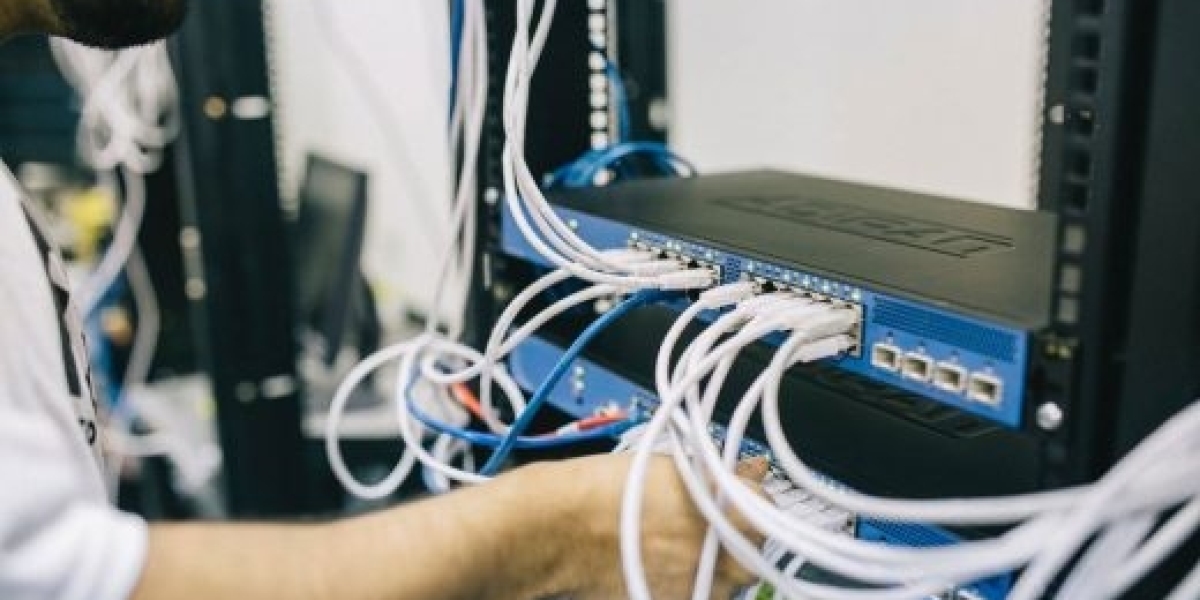
Structured cabling is the organized design and installation of a cabling system that supports multiple hardware uses in one streamlined infrastructure. It serves as the foundation of all communication systems in a building or campus — including internet, telephony, security systems, and data transfer.
Instead of a messy tangle of wires for every new device or function, structured cabling provides a neat, scalable, and future-ready framework. In the Philippines, where businesses are rapidly digitizing and smart city projects are accelerating, structured cabling is now essential for efficiency and reliability.
Structured cabling is not just about neat wires — it’s about ensuring high-speed data flow, minimizing downtime, and reducing future maintenance costs.
2. Why Structured Cabling Is Crucial for Modern Infrastructure
Modern organizations rely on fast, stable, and secure networks. A poorly designed cabling system leads to:
Slow internet speeds
Frequent disconnections
High maintenance costs
Limited scalability
Fire hazards due to improper routing
On the other hand, investing in structured cabling enables the following:
[Insight] Centralized control and flexibility
A structured system integrates all network devices under a single architecture. Upgrading or expanding becomes simple and cost-efficient.
[Tip] Future-proofing
Modern Cat6/Cat6a or fiber optic cabling supports speeds of up to 10 Gbps or more — ready for future tech like 5G, edge computing, and AI.
[Warning] Without structured cabling, businesses face higher IT troubleshooting time and safety risks in multi-floor setups.
[Use Case] In a Makati BPO center, shifting from unmanaged patchwork cabling to structured infrastructure reduced downtime by 80% and improved network speed consistency across all floors.
3. Components of a Structured Cabling System
A structured cabling system is composed of standardized elements that work together to deliver a seamless communication and data network. Whether for a single building, multi-site office, or a smart city deployment, the core components remain the same.
Key components include:
[Component] Horizontal Cabling
Runs from the telecommunications room to individual outlets in work areas
Usually Cat5e, Cat6, or Cat6a copper cables or fiber optics
[Component] Backbone Cabling (Vertical Cabling)
Connects equipment rooms and telecommunications rooms across floors or buildings
Often uses fiber optic cabling for long-distance, high-speed transmission
[Component] Patch Panels
Serve as central points where cables terminate and can be easily reconfigured
Allow quick identification and maintenance
[Component] Racks and Cabinets
House switches, routers, servers, and patch panels
Improve airflow, cable management, and physical security
[Component] Faceplates and Outlets
Provide access points for end-user devices (PCs, phones, printers)
[Component] Cable Management Systems
Includes trays, conduits, ties, and raceways
Ensures neat, labeled, and separated runs to avoid interference and overheating
[Tip] A good structured cabling layout is modular, meaning you can easily scale, repair, or isolate problems without disrupting the entire system.
4. Benefits for Businesses, Schools, and Government
Structured cabling is not just for IT rooms. It supports the entire operational backbone of modern institutions. Here's why organizations in the Philippines — from SMEs to LGUs — are making the switch:
[Benefit] Reliable Network Performance
Structured cabling reduces packet loss, disconnections, and signal degradation. This results in stable connectivity for all digital systems, including VoIP, Wi-Fi access points, and security cameras.
[Benefit] Simplified Troubleshooting and Maintenance
When problems arise, IT teams can isolate issues quickly using labeled patch panels and racks — minimizing downtime.
[Benefit] Lower Long-Term Costs
Although structured cabling may seem expensive up front, it significantly reduces:
Downtime-related losses
Future upgrade costs
Risk of costly electrical repairs
[Benefit] High Scalability
As your organization grows, new devices or network nodes can be added without major rewiring or disruptions.
[Benefit] Supports Smart Systems
For property developers and LGUs, structured cabling enables integration with:
Smart lighting and energy meters
Public Wi-Fi zones
IoT-based CCTV and access control
e-Governance platforms
[Use Case]
A public high school in Cebu upgraded to structured Cat6 cabling to support a campus-wide e-learning network. The result: zero downtime during exams, smoother LMS access, and the ability to deploy smart attendance tracking.
5. Structured Cabling Standards in the Philippines
To ensure quality, safety, and interoperability, structured cabling must follow internationally recognized standards — many of which are also adopted by Philippine IT and construction codes.
Here are the key standards:
[Standard] ANSI/TIA-568
The core cabling standard that defines categories of copper cabling (Cat5e, Cat6, Cat6a) and performance specifications for data transmission. Widely referenced by telcos and commercial installers.
[Standard] ISO/IEC 11801
An international standard for generic cabling in commercial buildings — applicable in BPO offices, government centers, and universities.
[Standard] BICSI Guidelines
Published by the Building Industry Consulting Service International (BICSI), offering best practices on installation, testing, documentation, and labeling.
[Local Compliance]
In the Philippines, structured cabling installations must also comply with:
Philippine Electrical Code (PEC)
National Building Code (NBC)
ICT standards defined by the Department of Information and Communications Technology (DICT)
[Tip] When choosing a service provider, ask if they are BICSI-certified or trained under DICT digital infrastructure guidelines.
6. Use Cases: Offices, Data Centers, Smart Cities
Structured cabling is the backbone of digital transformation. Here’s how it’s being deployed across different sectors in the Philippines:
? Corporate Offices and BPO Centers
Cat6 cabling for high-speed workstations
Dedicated VLAN setups for HR, Finance, Operations
Centralized server and telecom rooms
[Use Case] In Ortigas, a multinational BPO uses structured fiber optic cabling between its 15-floor data distribution rooms — minimizing latency and ensuring seamless voice traffic.
? Schools and Universities
Support for e-learning systems and campus-wide Wi-Fi
Cabling for smart classrooms with CCTV and biometric access
Low-voltage cabling for bell systems, PAs, and smart boards
?️ Government Buildings
Structured cabling supports national ID systems, e-governance terminals, and 24/7 security systems
Centralized data center integration with LGU networks
[Tip] LGUs applying for smart barangay funding under DICT should prepare structured cabling blueprints in their proposals.
?️ Smart Cities and Barangay Networks
Fiber runs connecting CCTV, solar-powered street lights, environmental sensors
Integration with municipal command centers
Future-proofed for AI-driven surveillance and analytics
[Use Case] In Taguig City, a smart barangay pilot project used structured outdoor cabling to link weather sensors, free Wi-Fi APs, and digital notice boards — all managed from a local dashboard.
7. How to Choose a Structured Cabling Provider
Choosing the right cabling contractor is as important as the hardware itself. A poor installation can ruin even the most expensive components. Here’s how to evaluate providers in the Philippine market:
[Checklist] Key Selection Criteria
1. Certification and Experience
Look for BICSI-certified installers or DICT-accredited firms
Ask about past projects (e.g., hospitals, LGUs, BPOs)
2. Compliance with Standards
Ensure adherence to ANSI/TIA, ISO/IEC, PEC, and local building codes
Providers should document all cable tests and mappings
3. Warranty and Post-Installation Support
Good providers offer 10–25 year warranty on parts and installation
Should include maintenance, labeling, and troubleshooting support
4. Scalability Planning
Ask if their layout allows for future upgrades (e.g., from Cat6 to fiber)
Cabling should support your projected growth for at least 5 years
5. Professional Documentation
A professional vendor will provide you with a cabling blueprint, rack diagrams, labeling guide, and test results
6. On-site Inspection and Simulation
Reputable teams conduct a full site survey before quoting
Ask for a simulated network layout based on your expected device count
8. Top Structured Cabling Providers in the Philippines (2025)
Here are leading players offering commercial-grade structured cabling services nationwide or regionally:
1. Suniway Structured Cabling Solutions
Coverage: Luzon and Visayas
Specialties:
Fiber and copper hybrid setups
Smart city-ready cabling (for CCTV, solar, Wi-Fi)
Community deployments in schools and barangays
Highlights:
DICT-compliant documentation
Free site survey for LGU clients
Bundled with cloud, fiber, and surveillance systems
2. E-Data Services
Location: Metro Manila
Specialties:
Office network cabling
Telco-grade patch panels and server rack design
Highlights: Known for clear pricing, timely installations
3. ExcelCom Cabling
Location: Cebu and Mindanao
Specialties:
Data center cabling, VOIP
24/7 maintenance contracts
4. Wirewerks Philippines
Location: NCR + Region III
Specialties:
Copper and fiber backbone systems
Structured cabling + power backup design
Highlights: Cat6A and shielded cabling available
9. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Structured Cabling
Q1: What is the difference between structured cabling and traditional cabling?
Structured cabling is a standardized, organized network of cables that supports multiple data and voice systems across a building or campus. Traditional cabling is often ad-hoc, unplanned, and harder to maintain or scale.
Q2: How much does structured cabling cost in the Philippines?
Pricing varies depending on building size, number of outlets, cable type, and labor.
Small office (10–20 users): ₱50,000 – ₱120,000
Mid-sized floor (50+ users): ₱200,000 – ₱500,000
Smart building or campus: ₱500,000 and above
Always request a site inspection for an accurate quote.
Q3: What type of cable should I use — Cat5e, Cat6, Cat6a, or fiber?
Cat5e: Budget choice, up to 100 Mbps
Cat6: Standard for modern offices (up to 1 Gbps)
Cat6a: Supports up to 10 Gbps, better shielding
Fiber: Best for long-distance or backbone cabling
Recommendation: Use Cat6 at minimum in 2025 deployments.
Q4: Can structured cabling support both voice and data?
Yes. Structured cabling systems are designed to handle Ethernet, VoIP, CCTV, access control, and other low-voltage systems through a unified infrastructure.
Q5: How long does installation take?
Small office: 2–5 days
Multi-floor buildings: 1–3 weeks
Timelines depend on site readiness, permits, and material availability.
10. Conclusion: Build a Future-Ready Network
In the era of digital transformation, remote work, and smart infrastructure, structured cabling is no longer optional — it's essential. Whether you're managing a call center in Ortigas, upgrading a public school in Leyte, or wiring a municipal command center in Davao, investing in a standardized, scalable cabling system is one of the smartest IT decisions you can make.
From faster internet speeds and lower maintenance costs to seamless integration with smart systems, structured cabling lays the digital foundation of every modern operation.
[Action Step] Ready to upgrade your connectivity backbone?
Choose a structured cabling service provider in the Philippines that delivers quality, compliance, and future-ready performance — like Suniway, trusted by LGUs, SMEs, and smart city developers nationwide.