When it comes to metal fabrication and repair, the welding gun stands as one of the most essential tools for professionals and hobbyists alike. Its role in joining metals with precision and strength cannot be overstated. Understanding the welding gun, how it works, and the applications it serves is key to maximizing productivity and quality in welding projects.
What is a Welding Gun?
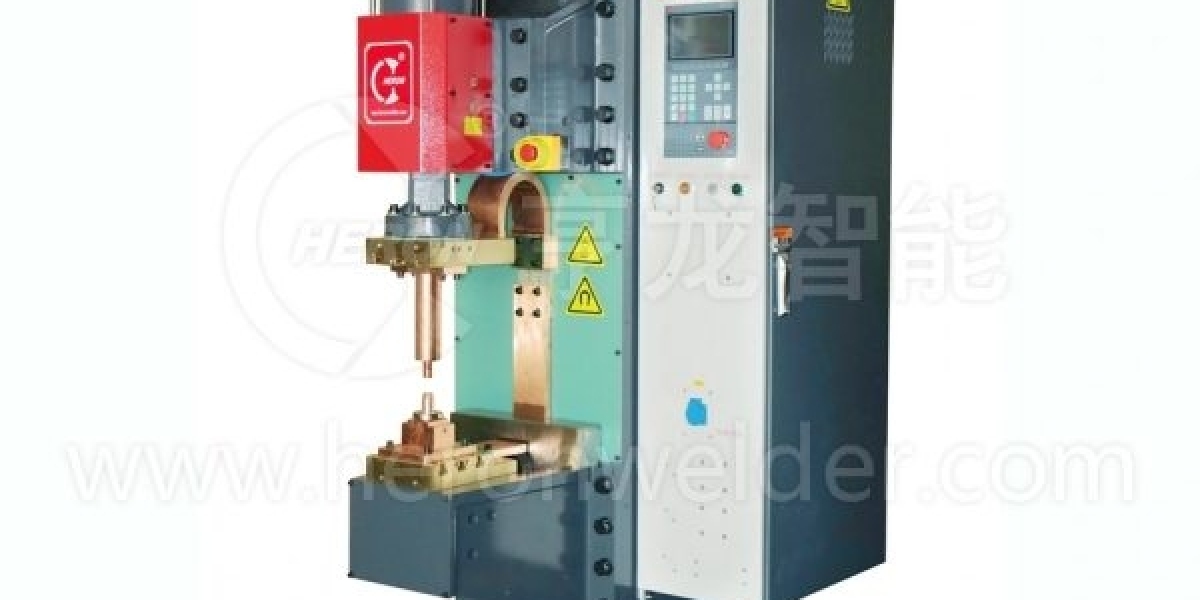
A welding gun is a handheld device designed to deliver heat and filler material to a precise point, allowing metals to fuse together. Depending on the type of welding process, the gun may use electric arcs, plasma, or other heat sources. It is connected to a power supply, and in some cases, to a gas source, to facilitate the welding process.
The design of a welding gun is tailored to ensure that operators have control over the weld, enabling them to achieve consistent results. From industrial workshops to home garages, the versatility of welding guns allows for a wide range of applications.
Types of Welding Guns
Welding guns come in different forms depending on the welding technique being used. Some of the most common types include:
MIG Welding Gun (Metal Inert Gas): Uses a continuous wire feed and inert gas to create clean and efficient welds.
TIG Welding Gun (Tungsten Inert Gas): Offers precise control for thin materials and intricate work.
Plasma Cutting Gun: Utilized for cutting metals rather than joining, providing sharp, accurate cuts.
Stick Welding Gun: Often used in outdoor or rugged environments for versatile metal joining.
Each type of welding gun is designed to meet the specific needs of a project, ensuring that professionals can maintain quality and precision regardless of the material or working conditions.
How a Welding Gun Works
At its core, a welding gun functions by generating intense heat to melt the base metal and, if needed, a filler material. The heat source can be an electric arc or a plasma stream, depending on the type of welding gun. The operator guides the gun along the seam, ensuring a controlled and consistent application of heat.
In MIG and TIG processes, the welding gun is also responsible for delivering shielding gas. This gas protects the weld pool from contamination by oxygen and other elements in the air, which could weaken the weld or create imperfections. Proper handling of the welding gun ensures a strong, durable bond between metal surfaces.
Applications of Welding Guns
The welding gun is used in a wide array of industries and applications. Automotive manufacturing, construction, shipbuilding, and aerospace are just a few sectors where welding guns play a pivotal role.
In automotive repair, a welding gun is often used to join body panels, repair frames, and fabricate custom parts. In construction, it helps in creating steel frameworks and reinforcing structures. Metal artisans and hobbyists also rely on welding guns to craft sculptures, furniture, and tools.
Beyond industrial uses, welding guns have also become integral to DIY projects and small-scale fabrication. Their accessibility allows skilled individuals to produce professional-grade results from workshops at home.
Safety Considerations
While the welding gun is an incredibly powerful tool, safety is paramount. Operators should always wear protective gear, including helmets with proper shading, gloves, and flame-resistant clothing. Proper ventilation is also crucial to avoid inhaling fumes and gases produced during welding.
Regular maintenance of the welding gun ensures optimal performance. Cleaning nozzles, checking electrical connections, and inspecting the trigger mechanism can prevent accidents and prolong the life of the equipment.
Tips for Efficient Use
Maximizing the effectiveness of a welding gun requires practice and understanding. Here are some essential tips:
Maintain a steady hand: Consistency in movement ensures uniform welds.
Adjust settings properly: Voltage, wire feed speed, and gas flow must match the material being welded.
Position correctly: Angling the gun correctly improves penetration and weld quality.
Regular inspection: Check for wear on tips and nozzles to prevent inconsistent performance.
Practice safety protocols: Keep fire extinguishers nearby and avoid flammable environments.
By following these practices, operators can achieve professional results and extend the lifespan of their welding gun.
Future of Welding Guns
The evolution of the welding gun continues as technology advances. Modern welding guns are becoming lighter, more ergonomic, and more precise. Innovations in automation, robotics, and smart controls are transforming the way metal fabrication is approached.
As industries demand faster production and higher quality, welding guns will play an even more central role in shaping the future of manufacturing. Integration with computer-aided systems and real-time monitoring ensures that welds are not only strong but also consistently perfect across large-scale projects.
Final Thoughts
The welding gun is more than just a tool; it is the bridge between raw metal and finished creation. Its versatility, precision, and indispensability in metalwork make it an essential part of any fabrication setup. Whether in industrial workshops or home garages, mastering the welding gun unlocks a world of possibilities for crafting, repairing, and building durable metal structures.